Marsilea: the 4-leaf clover fern
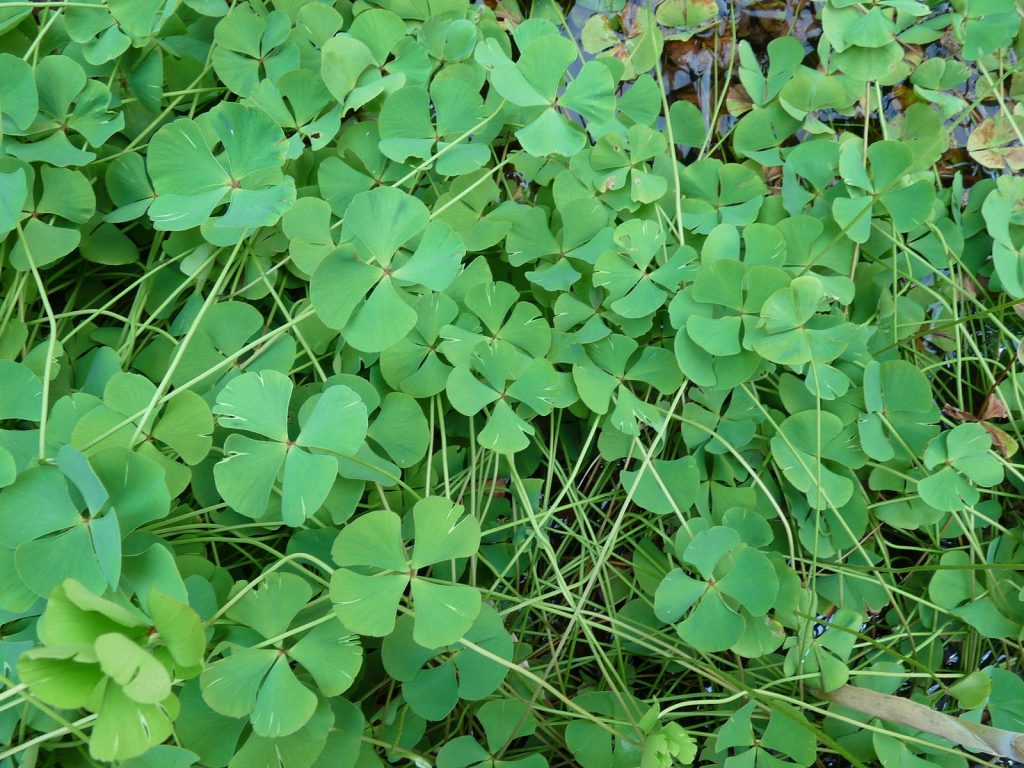

Marsilea is a genus of ferns that don’t look much like fern s. Its leaves look more like a four-leaf clovers than the typical fern leaf. There are a number of species of Marsilea and it is common throughout temperate and subtropical regions of the world, usually growing in shallow water with a stem rooted to the bottom and leaves that extend up and float on the surface. In North America M. quadrifoliata is considered a weed, although it is commonly grown intentionally in water gardens. It is sometimes found emerging from moist soil as well.
Phylogeny and taxonomy
Marsilea is in a group (generally considered an order — the Salviniales) that is known as ‘water ferns’ in the Phylum Pterophyta (ferns), the group that includes most seedless vascular plants (the other group of seedless vascular plants are the clubmoss group, Lycopodiophyta). Some water ferns, including mosquito fern and azolla, are floating aquatic species, while Marsilea is rooted and can tolerate seasonally dry conditions.
Structure
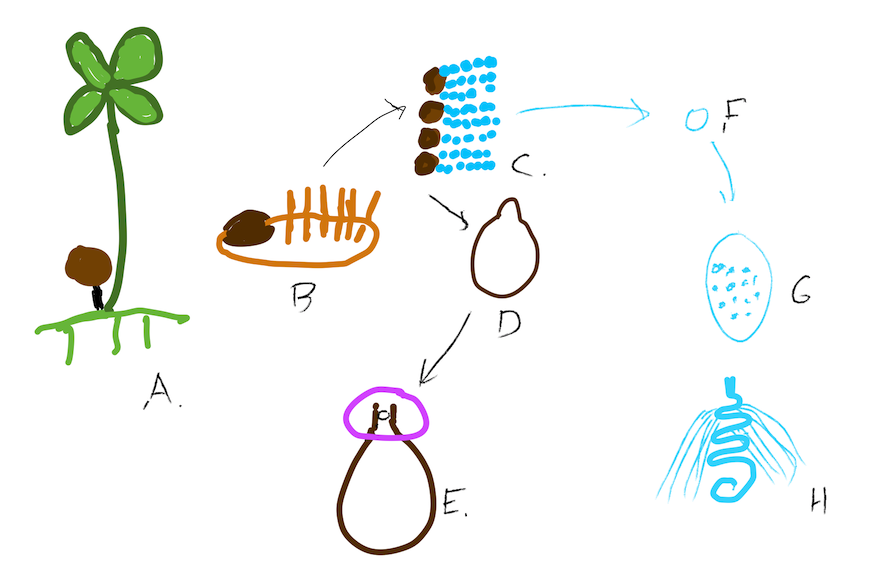
Marsilea produces a horizontally running stem across the surface of the substrate (which may be underwater). Like sensitive fern and some of the horsetails, water fern is dimorphic and the horizontal stem produces two types of leaves, green, photosynthetic leaves and non-photosynthetic leaves associated with reproduction. The vegetative leaves look like shamrocks. These elongate and make it to the surface of the water or, if growing on moist soil, grow to a height of ~ 10 cm. A second type of leaf is much smaller, with a shorter petiole ending in a sporocarp, a brown circular seed-like structure that dries out completely.
Sex and reproduction
Like all plants, Marsilea alternates between a haploid and diploid stage. And like all vascular plants, it is the diploid, spore producing, stage that is most visible. The sporocarp is seed-like in looks and behavior, but developmentally is something very different. The sporocarp is a highly modified spore-bearing leaf that develops to a certain point and then becomes dormant and dries out and is therefore capable of being dispersed. Eventually, when the hard coating of the sporocarp becomes scarred, either by mechanical forces (abrasion) or by biotic forces (decomposition), water can enter and hydrate the spore bearing leaf, which then emerges from the sporocarp. The leaf looks nothing like a regular leaf, it is very small and non-photosynthetic, but bears two types of sporangia, producing two types of spores: larger spores (megaspores) that develop into female gametophytes inside the spore case (endosporically) and smaller spores that release flagellated sperm.
Matter and energy
Marsilea sporophytes are photosynthetic autotrophs. The gametophytes live solely off material from the sporophyte incorporated in the mega and microspores.
Interactions
Marsilea sporocarps (the seed-like structures) are eaten by aboriginal Australians, although proper preparation is important. The plant produces an enzyme, thiaminase, that breaks down vitamin B1 and if this enzyme is not de-activated vitamin B1 deficiency and death can result. This same enzyme is also found in bracken fern, some horsetails and also in carp and goldfish.
Further Reading
- “Marsilea – Classification, Structure of Sporophyte, Reproduction, Structure of Gametophyte and Fertilization” by Prema Iswary. Good discussion of Marsilea biology.
Media Attributions
- Marsilea quadrifolia colony © Show_ryu is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

